Under normal circumstances, when we talk about titanium and titanium alloys, the titanium alloys here generally refer to TC4 alloy, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, which is a titanium alloy containing 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. It can be abbreviated as "six-aluminum-four-vanadium". The preparation process involves an aluminum thermal reaction, that is, by reducing vanadium pentoxide with aluminum to obtain vanadium-aluminum alloy.

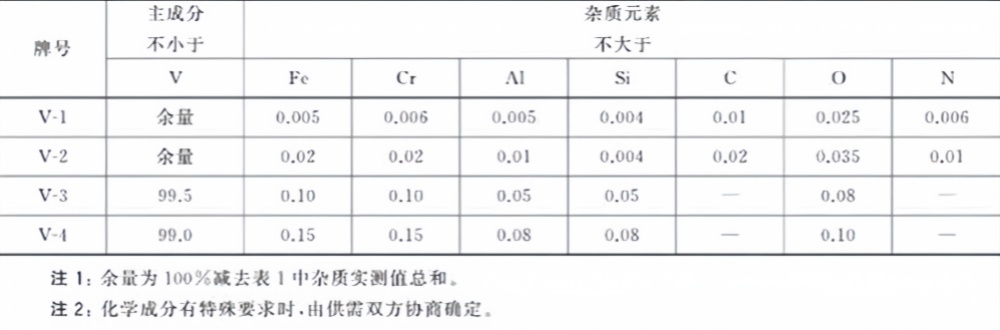
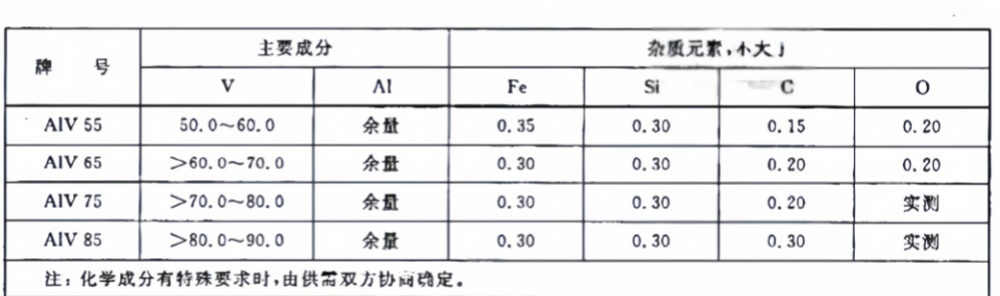
The amount of vanadium used in titanium alloys is inspected according to "YST 579-2006 Vanadium-Aluminum Intermediate Alloy" for incoming material. The manufacturer also follows this standard for production.
Aluminum (Al): Aluminum is one of the most commonly used additives in titanium alloys. It can form an α phase solid solution with titanium, increasing the strength and hardness of the titanium alloy. At the same time, the addition of aluminum can also reduce the density of the titanium alloy and improve its specific strength.

Vanadium (V): Vanadium is an important β stabilizing element in titanium alloys. By adjusting the amount of vanadium added, the ratio of α phase and β phase in the titanium alloy can be regulated, thereby optimizing the performance of the titanium alloy.

During the preparation of titanium alloys, the vanadium additive can form compounds with titanium. These compounds are dispersed in the titanium alloy and are strengthened by precipitation, improving the performance of the titanium alloy.

How can vanadium be added to titanium alloys? It is necessary to mix aluminum-vanadium alloy with aluminum beads, oxygen powder, etc. evenly and add them to the sponge titanium during the pressing electrode process.
Vanadium is a silver-gray metal. Its melting point is 1919 ± 2℃, and it belongs to the category of high-melting-point rare metals. Because the compounds of vanadium have various colors and are very beautiful, this new element was named "Vanadium" using the name of a beautiful goddess in Norse mythology, named Vanadis. In Chinese, it is named "钒" according to its phonetic translation.
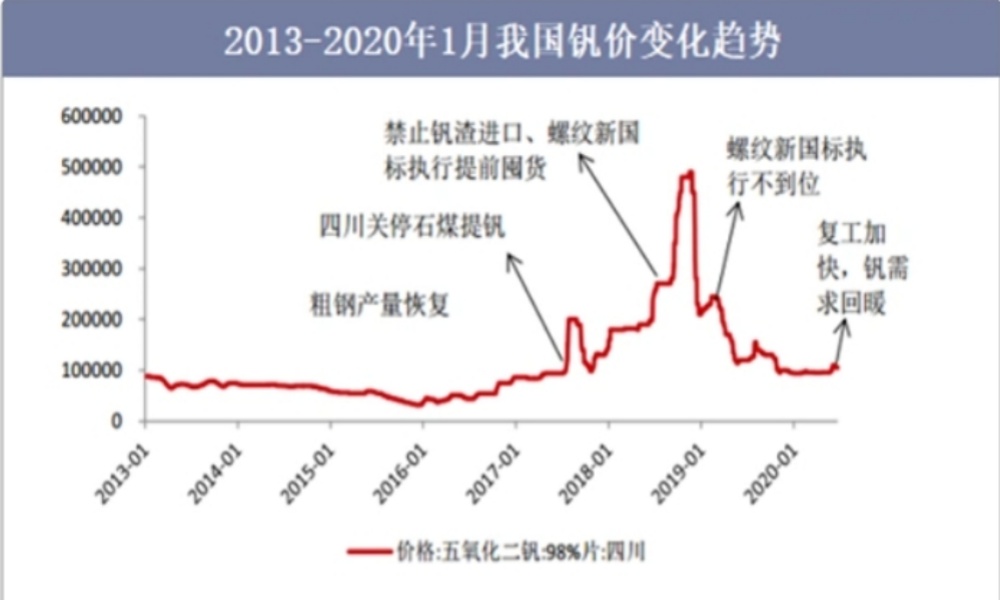
China is the country with the most abundant vanadium reserves in the world, accounting for more than one-third of the world's total. Among them, the Panxi area in Sichuan Province is known as the "Vanadium-Titanium Capital", famous for its rich vanadium-titanium magnetite resources.

Vanadium resources are widely distributed globally. 98% of the world's production comes from vanadium-titanium magnetite. According to the data, as of the end of 2017, the global proven vanadium reserves reached 200 million tons, and the proven reserves of China, Russia, South Africa, Australia, and the United States ranked in the top five. China's proven vanadium ore reserves reached 9 million tons, accounting for 45% of the global total.

The uses of vanadium are very extensive. Vanadium has important applications in the steel industry, metallurgical chemical industry, aerospace, national defense industry, medicine, pigments, glass, new energy batteries, etc. It is called "metal vitamin", "chemical bread", and "the essence of modern industry".